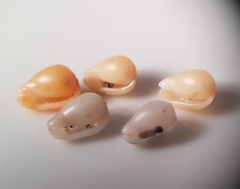
White garden snail
Theba pisana
Theba pisana is a species of small land snail belonging to the family Helicidae. It is commonly found in the Comunidad Valenciana, where it is often referred to as the "caracol moro" due to its prevalence and distinct features.
Theba pisana is distinguished by the following characteristics:
- Shell Appearance: The shell is globular and usually measures between 12-25 mm in diameter. It is often creamy white to light brown with darker spiral bands or spots, which serve as an excellent camouflage against its natural habitat.
- Habitat: This species thrives in a variety of environments, particularly in coastal areas, fields, and gardens. It is well-suited to dry and arid climates often found in the Mediterranean region.
- Behavior: Theba pisana is known for its climbing ability, often seen attaching itself to vegetation or even man-made structures. This behavior helps it avoid hot ground surfaces and conserve moisture during dry periods.
- Diet: Theba pisana is herbivorous, feeding on a wide range of plant materials, which can sometimes make it an agricultural pest, especially in areas with dense farmland.
- Reproduction: As a hermaphroditic species, each snail possesses both male and female reproductive organs, allowing them to exchange gametes and produce offspring efficiently in suitable conditions.
Theba pisana is not only significant in terms of biodiversity but also in ecological studies as an indicator species for environmental changes. Its presence and population dynamics can provide insights into local ecosystem health and climate variations.